You can use PowerShell to install Windows Updates automatically, unattended and simple. Neat, right? For this, you don’t have to have an enterprise environment with WSUS, or Windows Server, but since this is Sysadmins of the North, I assume you do. In this post I’m show you how to install Windows Updates with PowerShell and the PSWindowsUpdate module.
This post explains how to use PowerShell and the PSWindowsUpdate module to automatically install Windows Updates on your systems. For this, you don’t have to have an enterprise environment with WSUS, or Windows Server.
To being able to install Windows Updates with PowerShell, you need Powershell installed. Duh 🙂 Either 5.1 or 7.3, at the time of this writing. If you fulfill this requirement, you can install and use PSWindowsUpdate module. Windows Updates are easily installed from either Windows Update or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS).
Also read:
Install PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module
PSWindowsUpdate is a PowerShell module to install Windows Updates. There are more modules for this purpose, but this is the one I use and am used to. To make this module available, start a PowerShell instance as administrator.
Choose “Run as Administrator”.
If necessary, you first have to set the execution policy to RemoteSigned: Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned. After this you can install the module:
- If required:
Install-PackageProvider -Name NuGet -Force(works only with PowerShell 5.1, not PWSH 7) Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
When this command is successfully run (there is no confirmation), you can use Get-Command to list available cmdlets and aliases. Provide Get-Command with the -Module argument and module name:
Get-Command -Module PSWindowsUpdate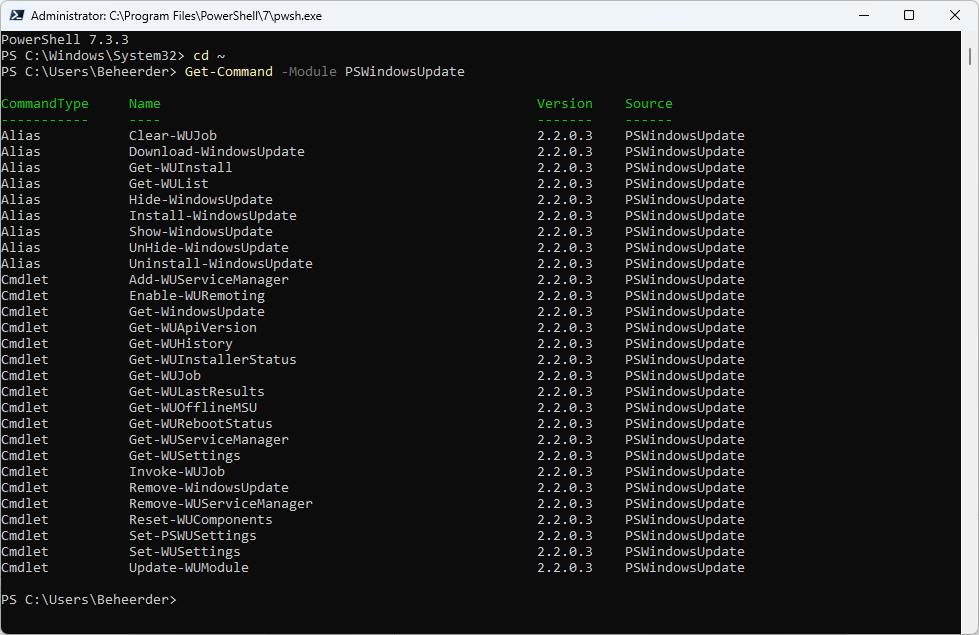
Get-Command -Module PSWindowsUpdate
CommandType Name Version Source
----------- ---- ------- ------
Alias Clear-WUJob 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Download-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Get-WUInstall 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Get-WUList 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Hide-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Install-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Show-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias UnHide-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Alias Uninstall-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Add-WUServiceManager 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Enable-WURemoting 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUApiVersion 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUHistory 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUInstallerStatus 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUJob 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WULastResults 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUOfflineMSU 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WURebootStatus 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUServiceManager 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Get-WUSettings 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Invoke-WUJob 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Remove-WindowsUpdate 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Remove-WUServiceManager 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Reset-WUComponents 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Set-PSWUSettings 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Set-WUSettings 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdate
Cmdlet Update-WUModule 2.2.0.3 PSWindowsUpdateAfterwards you verify installed Windows updates with PowerShell too.
Searching for available Windows Updates
Now you have PSWindowsUpdate installed and available, you want to search WSUS or Windows Update for available updates, right? Here’s how to search for available updates:
Get-WindowsUpdate
ComputerName Status KB Size Title
------------ ------ -- ---- -----
LAPTOPJANR ------- KB2267602 821MB Security Intelligence Update for Microsoft Defender Antivirus - KB2267602 (Ve…Scan for, or detect, new updates with Microsoft.Update.AutoUpdate COM-object in PowerShell: (new-object -Comobject Microsoft.Update.AutoUpdate).detectnow()
Download and install available Windows updates
After finding updates to install, you need to install them. That’s as easy as using Install-WindowsUpdate (which is an alias for Get-WindowsUpdate -Install):
- Download & Install (choose accept when requested):
Install-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602 -ForceDownloadThis accepts, downloads and installs the update. When in doubt, you can always execute the command with -ForceInstall later:
Install-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602 -ForceInstallA confirmation is given that the update has been accepted, downloaded and installed:
X ComputerName Result KB Size Title
- ------------ ------ -- ---- -----
1 DESKTOP-J... Accepted KB2267602 574MB Security Intelligence Update for Windows Defender Antivirus - KB2267602 (...
2 DESKTOP-J... Downloaded KB2267602 574MB Security Intelligence Update for Windows Defender Antivirus - KB2267602 (...
3 DESKTOP-J... Installed KB2267602 574MB Security Intelligence Update for Windows Defender Antivirus - KB2267602 (...You can do a lot more with PSWindowsUpdate module for PowerShell, like planning, dowloading and installing of updates. This may be perfect in your update routine. Install Windows Updates silently 🙂 See Get-Help Install-WindowsUpdate for more information and examples.
You can also search for updates all at once and specify whether all found updates should be accepted and installed. You can do this with -AcceptAll -Download -Install and, if necessary, -MicrosoftUpdate to indicate that you want to consult Microsoft Windows Update instead of, for example, a local WSUS.
If you are in a WSUS environment and want to search WindowsUpdate, use -WindowsUpdate command argument.
Get-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Download -Install -MicrosoftUpdate
X ComputerName Result KB Size Title
- ------------ ------ -- ---- -----
1 DESKTOP-J... Accepted KB4481252 13MB Microsoft Silverlight (KB4481252)
1 DESKTOP-J... Accepted KB3152281 48MB Click-to-Run Update Support
2 DESKTOP-J... Downloaded KB4481252 13MB Microsoft Silverlight (KB4481252)
2 DESKTOP-J... Downloaded KB3152281 48MB Click-to-Run Update Support
3 DESKTOP-J... Installed KB4481252 13MB Microsoft Silverlight (KB4481252)
3 DESKTOP-J... Installed KB3152281 48MB Click-to-Run Update SupportAlso read:
Schedule Windows Updates download and installation silently with PowerShell and PSWindowsUpdate
As said, you can use PSWindowsUpdate to schedule the download and installation of Windows Update, to make the process silent. Perfect! 🙂 Schedule updates for automatic installation, here is an example:
Invoke-WUJob -Script {
Import-Alias PSWindowsUpdate;
Install-WindowsUpdate -IgnoreUserInput -Verbose -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot | Out-File ~\log\PSWindowsUpdate-$(Get-Date -format "yyyyMMdd").log
} -Confirm:$false -Verbose -TriggerDate (Get-Date -Day 15 -Hour 12 -Minute 00 -Second 0)On a local computer, this creates an scheduled task with name “PSWindowsUpdate” to run on day 15, hour 12, minute 00 and second 0. A log is saved in ~\log with name PSWindowsUpdate-$(Get-Date -format "yyyyMMdd").log.
If you want to schedule Windows Updates on remote computers, use the -ComputerName parameter:
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName SRV01,SRV02,SRV03 -Script {
Import-Alias PSWindowsUpdate;
Install-WindowsUpdate -IgnoreUserInput -Verbose -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot | Out-File ~\log\PSWindowsUpdate-$(Get-Date -format "yyyyMMdd").log
} -Confirm:$false -Verbose -TriggerDate (Get-Date -Day 15 -Hour 12 -Minute 00 -Second 0)This goes perfectly with Get-ADComputer in your Active Directory Domain.
Start the Windows Update GUI screen directly from cmd.exe (or PowerShell) with the following command: %windir%\explorer.exe ms-settings:windowsupdate-action (&$env:windir\explorer.exe ms-settings:windowsupdate-action)
Check for Pending Reboot after Windows Update with PowerShell (Bonus!)
Need to check for a pending reboot after installing Windows Updates? Use the Windows Registry:
if((Get-Item "HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update\RebootRequired" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).Property) {
write-output "reboot pending"
}Instead of using Write-OutPut you can also perform a reboot action here: Restart-Computer -Force.
Two other registry locations you must check:
"HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Component Based Servicing\RebootPending"
"HKLM:SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\PendingFileRenameOperations"Conclusion installing Windows Updates using PSWindowsUpdate module in PowerShell
In this post I showed you how you can use PowerShell to install Windows Updates. Quickly and silently. This makes the use of PSWindowsUpdate module perfect for your day to day automation. The module even supports scheduling (on remote computers too!), it has the ability to search WSUS and Windows Update for updates, scheduling and performing the download and installation of updates, and it’s still being actively developed.
Summary
- You can install Windows Updates using PowerShell and the PSWindowsUpdate module without needing an enterprise environment.
- To begin, ensure you have PowerShell installed, either version 5.1 or 7.3, then install the PSWindowsUpdate module.
- Use commands like Install-WindowsUpdate to download and install updates easily; add -ForceInstall to bypass prompts if needed.
- You can schedule updates for silent installations using PowerShell, setting tasks for specific times on local or remote computers.
- The PSWindowsUpdate module supports searching for available updates and can manage reboot checks post-installation.

Did you like this post?
Please take a second to support Sysadmins of the North and donate!
Your generosity helps pay for the ongoing costs associated with running this website like coffee, hosting services, library mirrors, domain renewals, time for article research, and coffee, just to name a few.