
IIS backup and restore
Learn how to back up and restore IIS 10 webserver configuration with appcmd.exe and PowerShell
Technical SysOps blog, where topics include Sysadmin, DevOps, computers, servers, web, MySQL, database, virtualization, optimization and security
Technical SysOps blog, where topics include Sysadmin, DevOps, computers, servers, web, MySQL, database, virtualization, optimization and security

Learn how to back up and restore IIS 10 webserver configuration with appcmd.exe and PowerShell
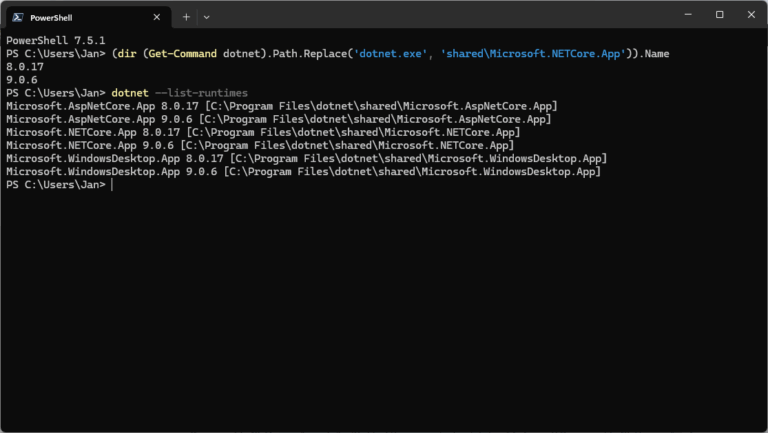
Users can install and run multiple .NET Framework versions on their computers. When you develop or deploy your app, you might need to know which .NET versions are installed on a machine and here is how to check the .NET version.

The AppCmd.exe command is your one-stop-shop for administering Windows Server IIS web servers. In combination with WinRM it is your Swiss Army knife for your daily routine. This post introduces appcmd and provides you with a lot of helpful appcmd…
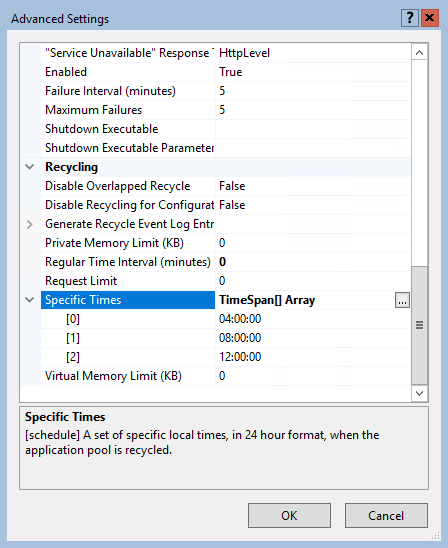
By default, an IIS application pool (or "AppPool") recycles on a regular time interval of 1740 minutes, or 29 hours. One reason for this time interval is that application pools don't recycle at the same moment every day (every day at 07.00 for example).

In this article you'll learn how to start all stopped application pools that have the ApplicationPool.AutoStart property set to $True using AppCmd.exe or PowerShell. This is something you often or occasionally have to perform on various servers, for example when an application pool hangs.

Windows Server IIS loves to tell the world that a website runs on IIS. It does so with the "Server:" header in the HTTP response, as shown below. In this post I'll show you how to remove HTTP response headers in Windows Server IIS. You don't want to give hackers too much information about your servers, right?.